Anatomy and Physiology - Planes, Movements and Defintions
Definitions
- Anatomy: - Branch of biological science that studies the structure of an organism.
- Physiology: - The science of the functioning of living organisms and of their component parts.
- Gross scale: - Large scale systemic and regional.
- Micro scale: - Small scale structure.
- Surface anatomy: - The features we can see or palpate (examine by touch) on the outside of the body. Prominent anatomical structures that we can see / palpate are called anatomical landmarks.
- Clinical anatomy: - Relates to how anatomical structures change with pathology or range of motion (the amount of movement allowed at a joint).
- Positional terminlogy: - Describes the position of structures in space / in relation to each other.
- Flexion: - involves ‘the bending of two adjacent body segments so that their two anterior/posterior surfaces are brought together’
(Palastanga & Soames, 2012, p3).
- Extension: - involves ‘the moving apart of two opposing surfaces’ or ‘movement beyond the neutral position’ (Palastanga & Soames, 2012, p3).
- Plantarflexion: - ‘Moving the top (dorsum) of the foot away from the anterior surface of the leg’.
- Dorsiflexion: - ‘Bringing the dorsum of the foot towards the anterior surface of the leg’.
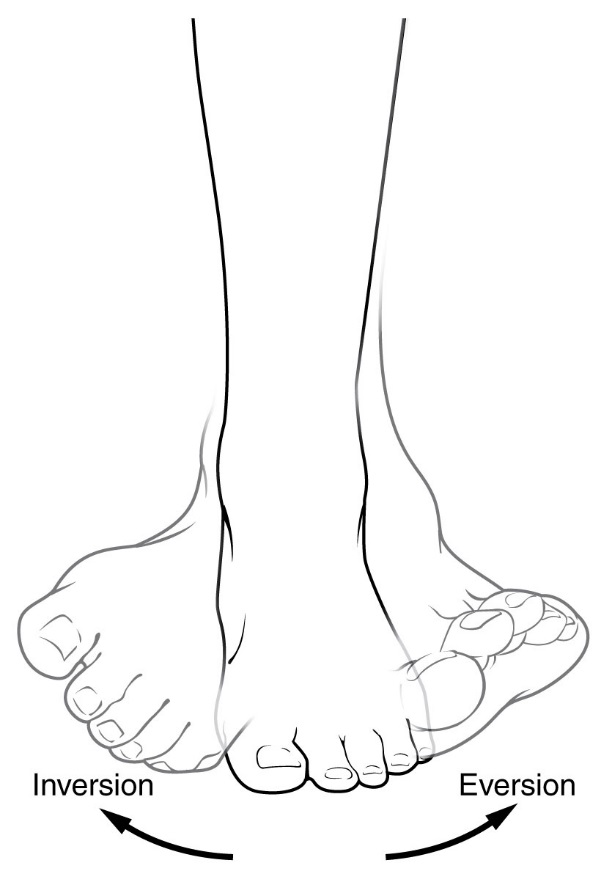
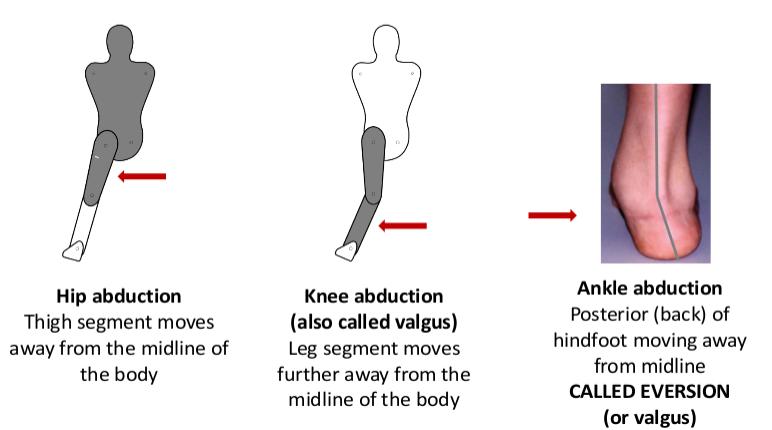
- Eversion/Valgus: - Posterior (back) of hindfoot moving away from midline.
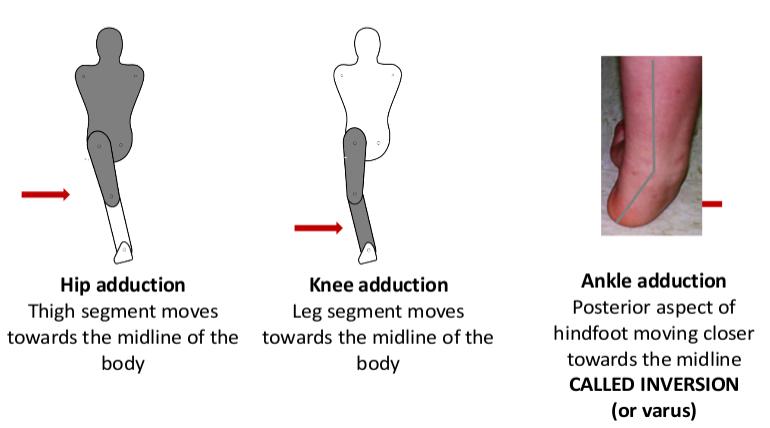
- Inversion/Varus: - Posterior aspect of hindfoot moving closer towards the midline.
- Abduction: - ‘The movement of a body segment such that it moves away from the midline of the body’ (Palastanga & Soames, 2012, p3).
- Adduction: - ‘The movement of a body segment in a coronal plane such that it moves towards the midline of the body’ (Palastanga & Soames, 2012, p3).
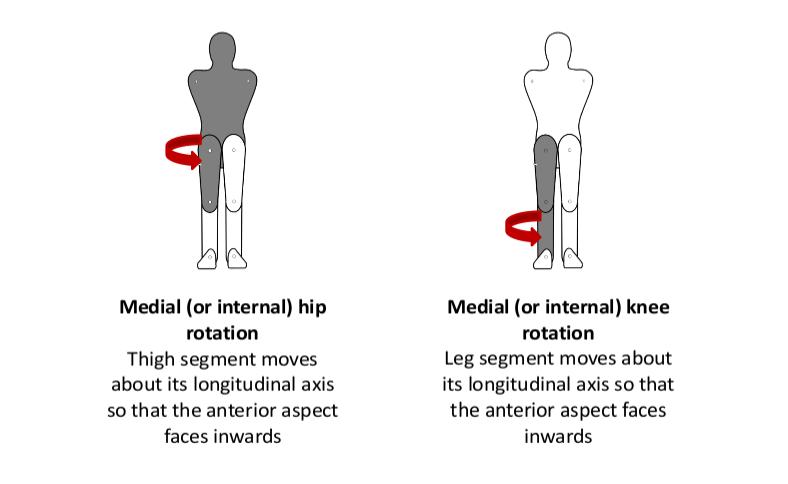
- Medial Rotation: - ‘Rotation of a limb segment about its longitudinal axis so that the anterior surface comes to face the midline of the body’ (Palastanga & Soames, 2012, p3).
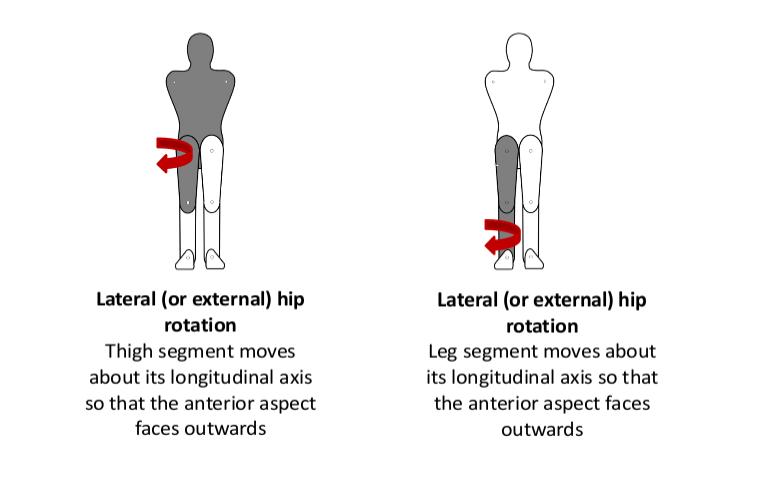
- Lateral rotation: - ‘Rotation of a limb segment about its longitudinal axis so that the anterior surface faces away from the midline’ (Palastanga & Soames, 2012, p3).
Positional Terminology Terms
Common words to describe the position of anatomical structures:
- Anterior: - To the front.
- Posterior: - To the back.
- Superior: - Above.
- Inferior: - Below.
- Lateral: - Away from the midline.
- Medial: - Towards the middle.
- Proximal: - Closer to the middle of the body.
- Distal: - Further away from the middle of the body.
- Superficial: - Closer to the surface of the body.
- Deep: - Further away from the surface of the body.
Anatomical Position
- Body standing erect
- Body facing forwards
- Legs together
- Feet parallel with toes pointing forwards
- Arms hanging loosely
- Palms of hands facing forwards (thumb lateral)
Anatomical Terminalogy relating to Bones
- Condyle: - a round protuberance that occurs at the end of some bones.
- Epicondyle: - the protuberance above a condyle at the end of an articulating bone.
- Fossa: - a depression or hollow.
- Foramen: - a hole.
- Process: - a thin prominence or protuberance.
- Ramus: - a thin process projecting from a bone.
- Spine: - a sharp process of a bone.
- Sulcus: - groove.
- Trabecula: - the thin bars of bony tissue in spongy bone.
- Lamella: - thin bands of calcified bone matrix.
- Trochlear: - an anatomical part having the structure or function of a pulley.
- Tuberosity: - a large rounded protuberance on a bone / expanded / pulled out.
- Facet: - plate like surface.
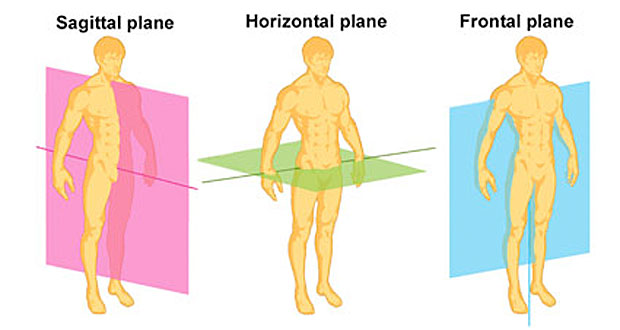
Planes of Motion
- Sagittal Plane: - can be seen when standing side on to someone.
- Coronal Plane: - can be seen when you stand in front of / behind someone.
- Transverse Plane: - can be seen when you stand above or below someone.
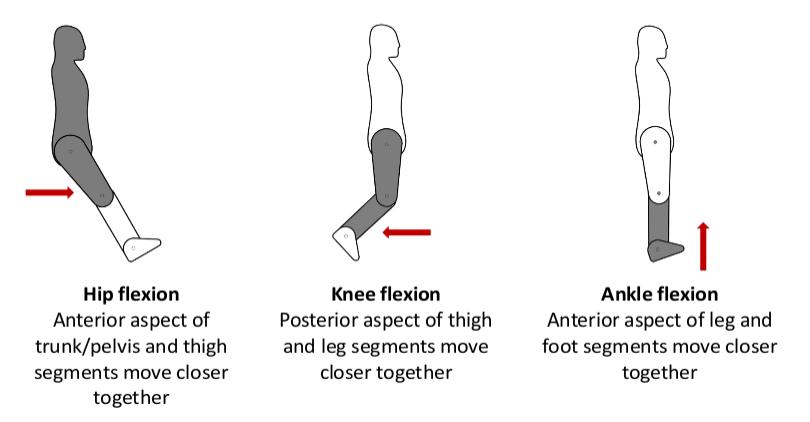
Movements
Flexion: - involves ‘the bending of two adjacent body segments so that their two anterior/posterior surfaces are brought together’ (Palastanga & Soames, 2012, p3).
- Hip flexion
- Knee flexion
- Ankle flexion
- Plantarflexion.
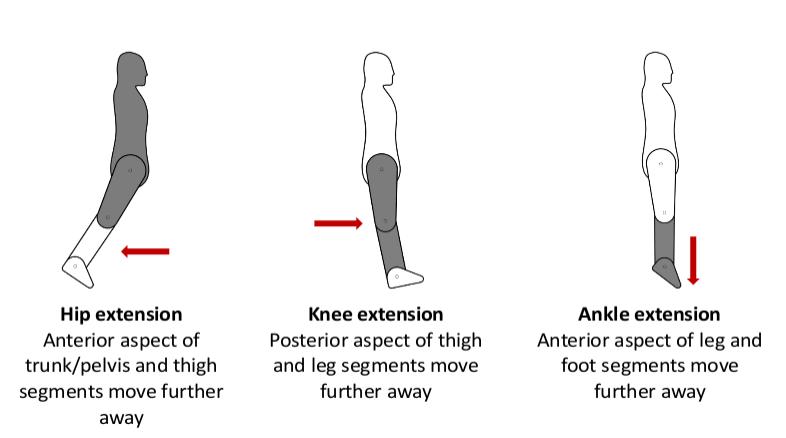
Extension: - involves ‘the moving apart of two opposing surfaces’ or ‘movement beyond the neutral position’ (Palastanga & Soames, 2012, p3).
- Hip extension
- Knee extension
- Ankle extension
- Dorsiflexion.
Abduction: - ‘The movement of a body segment such that it moves away from the midline of the body’ (Palastanga & Soames, 2012, p3).
- Hip abduction
- Knee abduction
- Ankle abduction.
Adduction: - ‘The movement of a body segment in a coronal plane such that it moves towards the midline of the body’ (Palastanga & Soames, 2012, p3).
- Hip adduction
- Knee adduction
- Ankle adduction
Medial Rotation: - ‘Rotation of a limb segment about its longitudinal axis so that the anterior surface comes to face the midline of the body’ (Palastanga & Soames, 2012, p3).
- Medial (internal) hip rotation
- Medial (internal) knee rotation.
Lateral rotation: - ‘Rotation of a limb segment about its longitudinal axis so that the anterior surface faces away from the midline’ (Palastanga & Soames, 2012, p3).
- Lateral (external) hip rotation
- Lateral (external) knee rotation.
Dorsiflexion (Extension): - ‘Bringing the dorsum of the foot towards the anterior surface of the leg’.
Plantarflexion (Flexion): - ‘Moving the top (dorsum) of the foot away from the anterior surface of the leg’.
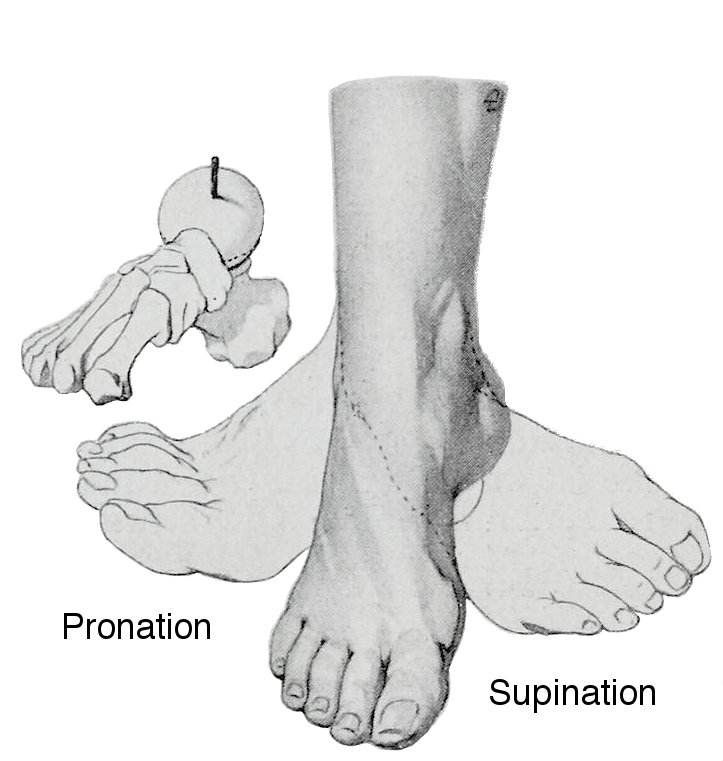
Pronation:: - Pronation of the foot is turning of the sole outwards, so that weight is borne on the medial part of the foot.
Supination: - Supination of the foot is turning of the sole of the foot inwards, shifting weight to the lateral edge.
Eversion: - Tilting the foot away from the midline of the body.
Inversion: - Tilting the foot towards the midline of the body.