Diabetes and PVD
Introduction
Prevalence:
- 4.8 Million UK pop.
- 5 Million by 2025
Issue:
- Glucose management issue
Types:
- Type 1: Genetic
- Type 2: Bad diet and lack of exercise
- Other
Body Vascular Anatomy
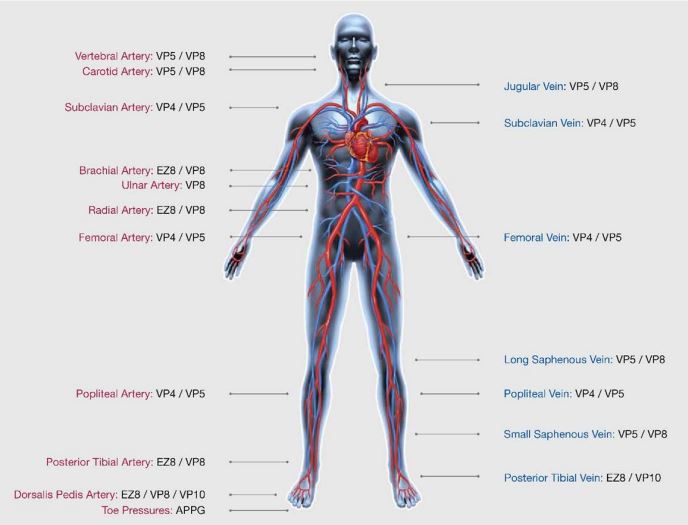
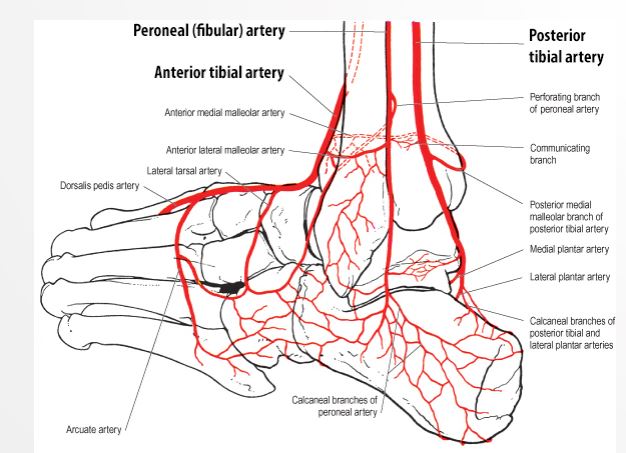
Foot Vascular Anatomy
Diabetes Mellitus
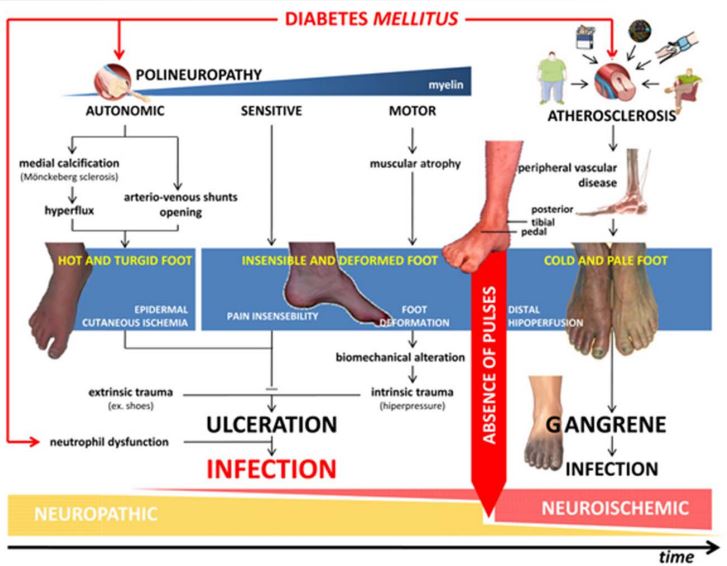
Diabetes Neuropathy
Neuropathy = nerve damage
NCS = nerve conduction
Vibration, Pressure/Touch and Motor/Reflex are the most common tests
PVD
- What is PVD?
- Arterial
- Venous
- Lymphatic
- Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
- Intermittent Claudication
- Critical Limb Ischaemia
- Gangrene
Effects of PVD
- Pain
- Callus
- Numbness
- Deformity
- Ulcers
- Gangrene
- Neuropathy (nerve damage)
- Ischemia (reduced blood supply)
Diagnosis
Signs and Symptoms
- Intermittent Claudication
- Rest Pain
- Numbed/dull leg
- Regularity
- Symmetry
- Strength
- Is this subjective?
- Regularity
- Symmetry
- Strength
- Is this objective?
Doppler Ultrasound Probe Positioning
Which Pulses should be assessed
- All guidelines concur that at least 2 pulses should be assessed for each foot.
Normally these are:
- posterior tibial,
- dorsalis pedis
- anterior tibial.
However, NICE guidance recommends that they should always include the peroneal pulse as this may be the only one present in some people, particularly those with diabetes (NICE, 2012).
Ankle-brachial Pressure Index (ABPI) Calculation
ABPI Interpretation
| ABPI | Diagnosis |
|---|---|
| < 0.5 | Severe PAD |
| 0.5 - 0.7 | Moderate PAD |
| 0.7 - 0.9 | Mild PAD |
| 0.9 - 1.3 | Normal |
| > 1.3 | Calcification? |
ABPI in Diabetes
- Regularity
- Symmetry
- Strength
- Is this objective?
Toe Brachial Index (TBI)
TBI > 0.7 = normal
Rest pain
- often in patients with TBI < 0.15
- absolute pressure in the toes of 20-30 mmHg
- Microcirculation
- Very localised
- TcPO2 > 50 mmHg = normal
- Determine Amputation Level
- Determine Healing Potential
- Poor chances if <30mmHG
Arterial Duplex
- Regularity
- Symmetry
- Strength
- Is this objective?
CT Angiography
- Regularity
- Symmetry
- Strength
- Is this objective?
Toe Brachial Index (TBI)
- Regularity
- Symmetry
- Strength
- Is this objective?
NHS Integrated Care Pathway
Referral Pathway
Treatments for PVDS
| Conservative | Medical | Surgical | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Exercise | Peripheral Vasodilators | Angioplasty/Stent |
| Treatment | Managing your risk factors | Anti-Platelet medication, Statins | Bypass |
| Details | - High BP - Smoking Cessation - Diet - Diabetes Control | - cilostazol, nifedipine, naftidrofuryl oxalate (vasodilators) - aspirin or clopidogrel (antiplatelet) - Art/Rosuv/Simv STATINS |
Critical Limb Ischemia (CLI)
Only method of treatment is amputation - feet are black - muscle death due to lack of blood supply
P & 0 Consideration
- Materials
- Aims and Objectives
- Short term
- Long term
References
Soyoye, D. O., Ikem, R. T., Kolawole, B. A., Oluwadiya, K. S., Bolarinwa, R. A., & Adebayo, O. J. (2016). Prevalence and Correlates of Peripheral Arterial Disease in Nigerians with Type 2 Diabetes. Adv Med, 2016, 3529419. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3529419
Wang, Z., Wang, X., Hao, G., Chen, Z., Zhang, L., Shao, L.,… China hypertension survey, investigators. (2019). A national study of the prevalence and risk factors associated with peripheral arterial disease from China: The China Hypertension Survey, 2012-2015. Int J Cardiol, 275, 165–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2018.10.047
Pradeepa, R., Chella, S., Surendar, J., Indulekha, K., Anjana, R. M., & Mohan, V. (2014). Prevalence of peripheral vascular disease and its association with carotid intima-media thickness and arterial stiffness in type 2 diabetes: the Chennai urban rural epidemiology study (CURES 111). Diab Vasc Dis Res, 11(3), 190–200. https://doi.org/10.1177/1479164114524584
Felício, J. S., Koury, C. C., Abdallah Zahalan, N., de Souza Resende, F., Nascimento de Lemos, M., Jardim da Motta Corrêa Pinto, R., … Abrahão Neto, J. F. (2019). Ankle-brachial index and peripheral arterial disease: An evaluation including a type 2 diabetes mellitus drug-naive patients cohort. Diab Vasc Dis Res, 1479164119829385. https://doi.org/10.1177/1479164119829385
Urbano, L., Portilla, E., Munoz, W., Hofman, A., Sierra-Torres, C. H., Muñoz, W., … Sierra-Torres, C. H. (2018). Prevalence and risk factors associated with peripheral arterial disease in an adult population from Colombia. Arch Cardiol Mex, 88(2), 107–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acmx.2017.02.002
Okello, S., Millard, A., Owori, R., Asiimwe, S. B., Siedner, M. J., Rwebembera, J., … Annex, B. H. (2014). Prevalence of lower extremity peripheral artery disease among adult diabetes patients in southwestern Uganda. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 14 75 https://doi org/10 1186⁄1471-2261-14-75