Medical Device Certification Week 3
Course Details
- Assessment by coursework
- Peer assessed
- 1 document
- Technical file
- Hand-in date 12th December
Technical File: Get details from Kirstie - Spec
- Description
- Annex 1 checklist
- Verification
- Validation
- Clinicial evidence and evaluation
- —
Overview
Principles of getting a device to market: * Process is planned * Process is organised * Process is reviewed * Process is documented
Met by: * a quality system * thorough product testing
Regulatory requirements: * Europe - Medical Devices Regulation (CE Mark) * US - FDA * Japan - Ministry of Health and Welfare
Classification of Devices in Europe: * Class 1 -> * Class 2 ->
Compliance for Medical Devices
15 Steps to Compliance for Medical Devices: * Determine it is a medical device * Determine the scope of the device * Determine the device certification * Select a conformity assessment procedure * Identify applicable “essential requirements” * Product safety requirements - risk assessment * Implement as ISO 13485 QMS * Design Verification and Validation including - Performance evaluation - Usability Engineering - Clinical Evaluation and Clinical Investigation
- Assemble “Technical documentation”
- Apply the conformity assessment procedure (notified body assessment needed?)
- Affix “CE MARK”, Declaration of conformity, UDI and register with competent authority
- Appoint an authorised representative
- Review and update PMS and PMCF
- Plan for Unannounced Audits
CE MARK * Understand and comply with the regulations * Develop your device under a QMS and gain ISO 13485 * Develop your device in planned stages
ISO Standards: * ISO means international * Each country has slightly different ISO standards * “Mandatory” and “Where Applicable” standards * BSI Shop is a place to go to buy ISO standards
MDDEVS’s: * Guidance documents provided for companies where no ISO standards exists or as additional information
Medical Device vs IVD: * Medical devices touch/analyse the human directly * IVD analyses samples of human cells etc, something that comes out of the body * The definitions in the CE Regulations very much determine what is an IVD or MD - intended purpose and context of use very important * CE Regulations - MDR - IVDR
What is a quality management system? * QMS is a set of written procedures for every process
Positional Terminology Terms
Common words to describe the position of anatomical structures:
- Anterior: - To the front.
- Posterior: - To the back.
- Superior: - Above.
- Inferior: - Below.
- Lateral: - Away from the midline.
- Medial: - Towards the middle.
- Proximal: - Closer to the middle of the body.
- Distal: - Further away from the middle of the body.
- Superficial: - Closer to the surface of the body.
- Deep: - Further away from the surface of the body.
Anatomical Position
- Body standing erect
- Body facing forwards
- Legs together
- Feet parallel with toes pointing forwards
- Arms hanging loosely
- Palms of hands facing forwards (thumb lateral)
Anatomical Terminalogy relating to Bones
- Condyle: - a round protuberance that occurs at the end of some bones.
- Epicondyle: - the protuberance above a condyle at the end of an articulating bone.
- Fossa: - a depression or hollow.
- Foramen: - a hole.
- Process: - a thin prominence or protuberance.
- Ramus: - a thin process projecting from a bone.
- Spine: - a sharp process of a bone.
- Sulcus: - groove.
- Trabecula: - the thin bars of bony tissue in spongy bone.
- Lamella: - thin bands of calcified bone matrix.
- Trochlear: - an anatomical part having the structure or function of a pulley.
- Tuberosity: - a large rounded protuberance on a bone / expanded / pulled out.
- Facet: - plate like surface.
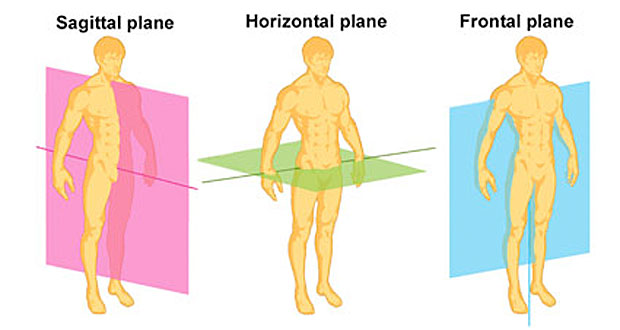
Planes of Motion
- Sagittal Plane: - can be seen when standing side on to someone.
- Coronal Plane: - can be seen when you stand in front of / behind someone.
- Transverse Plane: - can be seen when you stand above or below someone.
Movements
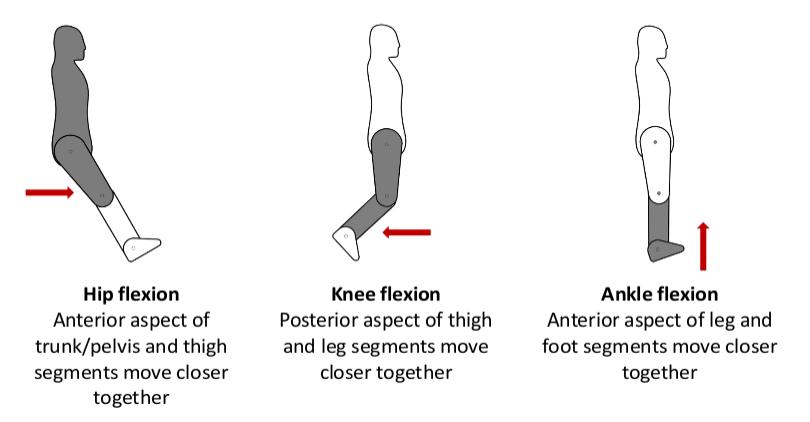
Flexion: - involves ‘the bending of two adjacent body segments so that their two anterior/posterior surfaces are brought together’ (Palastanga & Soames, 2012, p3).
- Hip flexion
- Knee flexion
- Ankle flexion
- Plantarflexion.
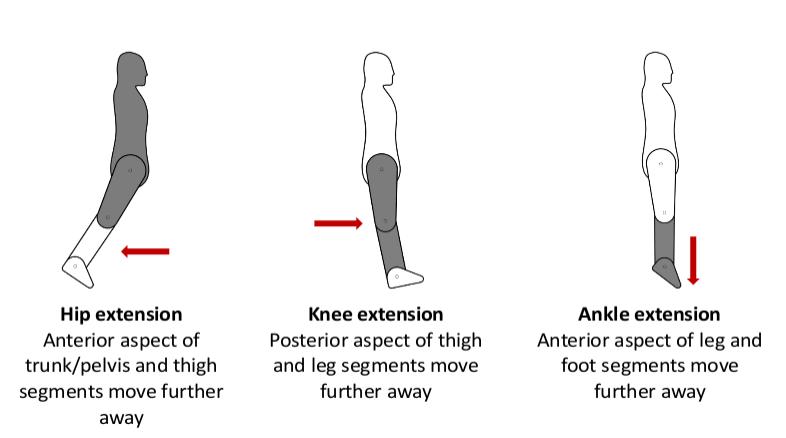
Extension: - involves ‘the moving apart of two opposing surfaces’ or ‘movement beyond the neutral position’ (Palastanga & Soames, 2012, p3).
- Hip extension
- Knee extension
- Ankle extension
- Dorsiflexion.
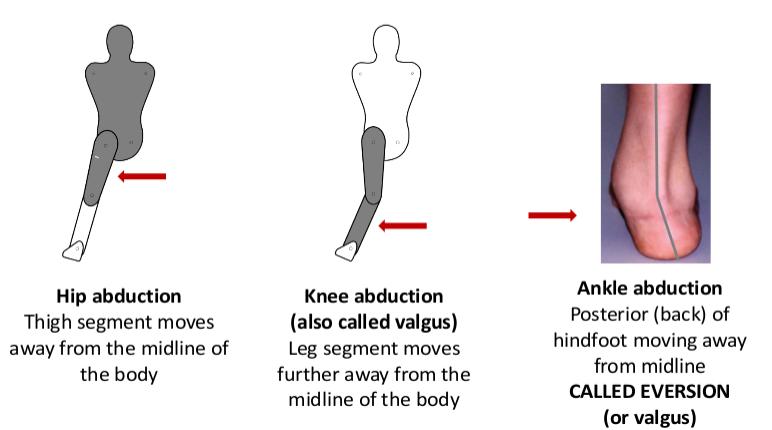
Abduction: - ‘The movement of a body segment such that it moves away from the midline of the body’ (Palastanga & Soames, 2012, p3).
- Hip abduction
- Knee abduction
- Ankle abduction.
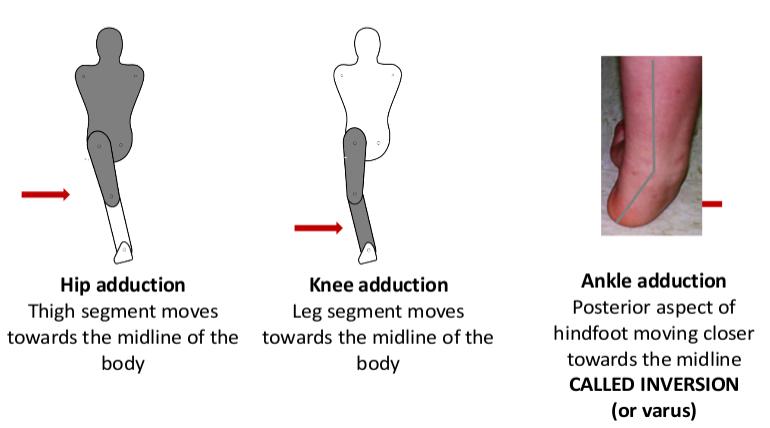
Adduction: - ‘The movement of a body segment in a coronal plane such that it moves towards the midline of the body’ (Palastanga & Soames, 2012, p3).
- Hip adduction
- Knee adduction
- Ankle adduction
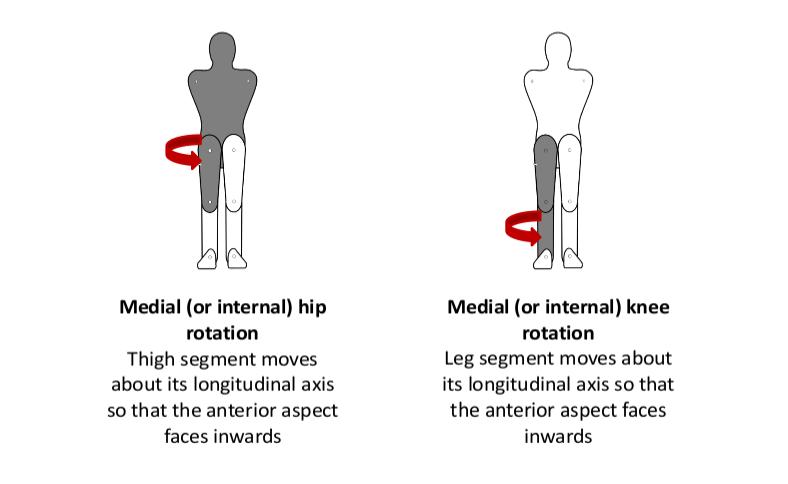
Medial Rotation: - ‘Rotation of a limb segment about its longitudinal axis so that the anterior surface comes to face the midline of the body’ (Palastanga & Soames, 2012, p3).
- Medial (internal) hip rotation
- Medial (internal) knee rotation.
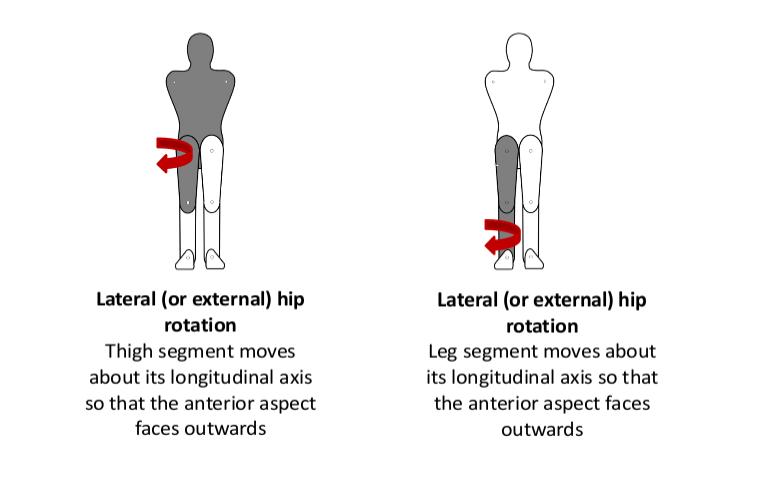
Lateral rotation: - ‘Rotation of a limb segment about its longitudinal axis so that the anterior surface faces away from the midline’ (Palastanga & Soames, 2012, p3).
- Lateral (external) hip rotation
- Lateral (external) knee rotation.
Other
Lecturer Warren Macdonald - w.macdonald@imperial.ac.uk