Running with Prosthetics
Introduction
Importance of Good Biomechanics
- Improve economy
- Minimise the cost of force absorption and generation
- Storage and return of elastic energy
- Reduce injury risk
- Reduce stress on the musculoskeletal system
- Maximise training time
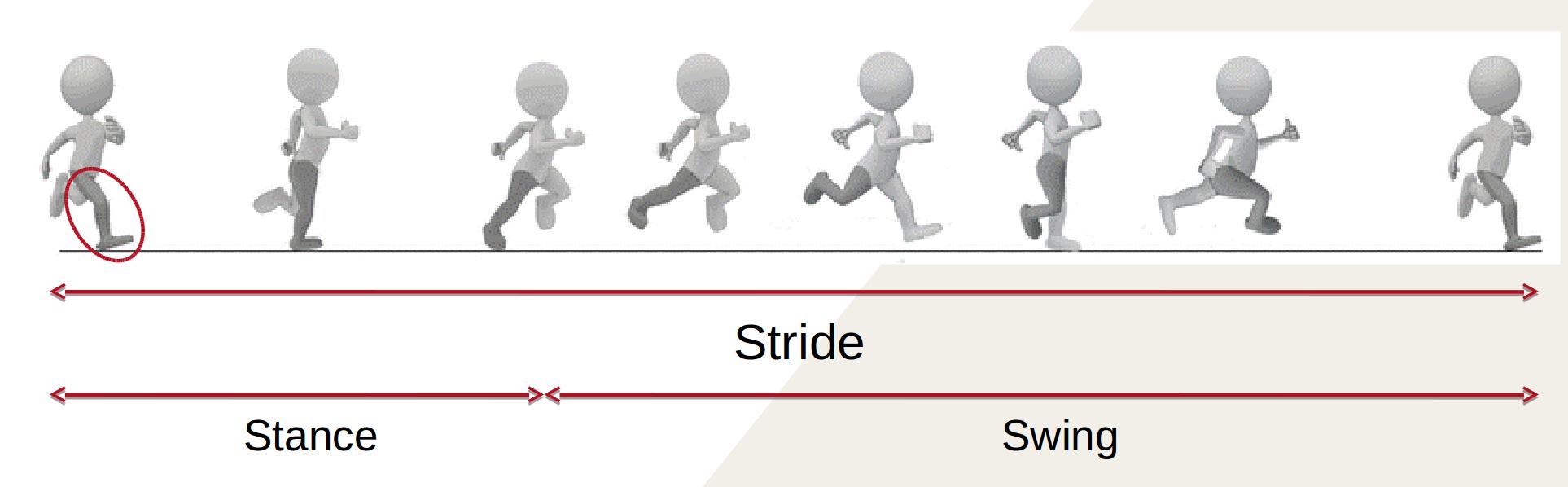
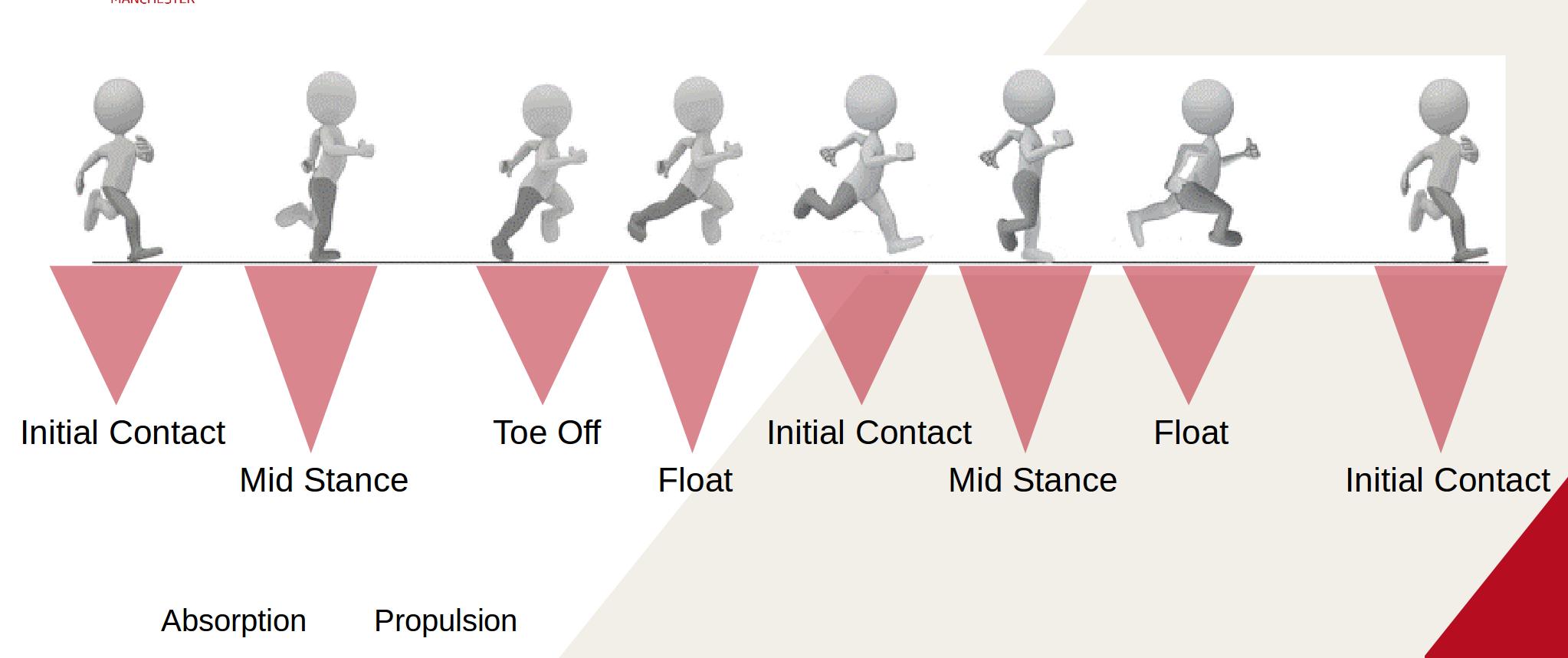
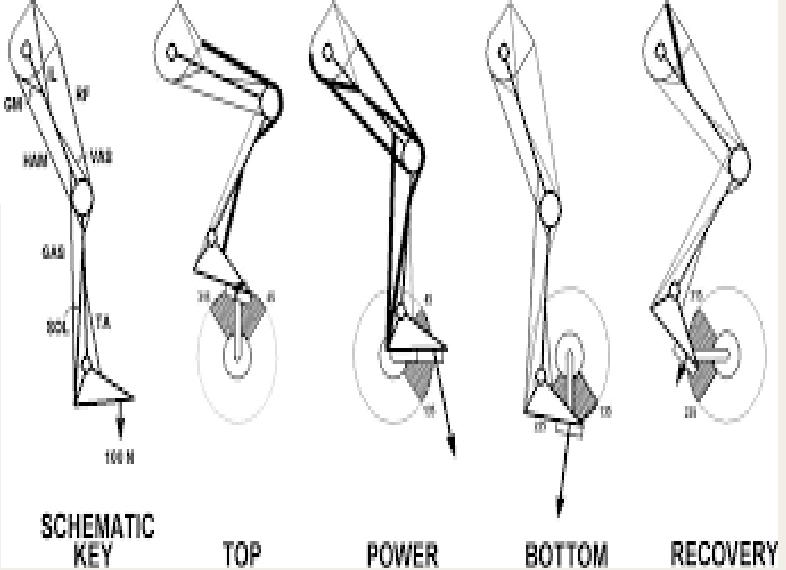
Breakdown of Gait
Centre of Mass Movement

Initial Contact
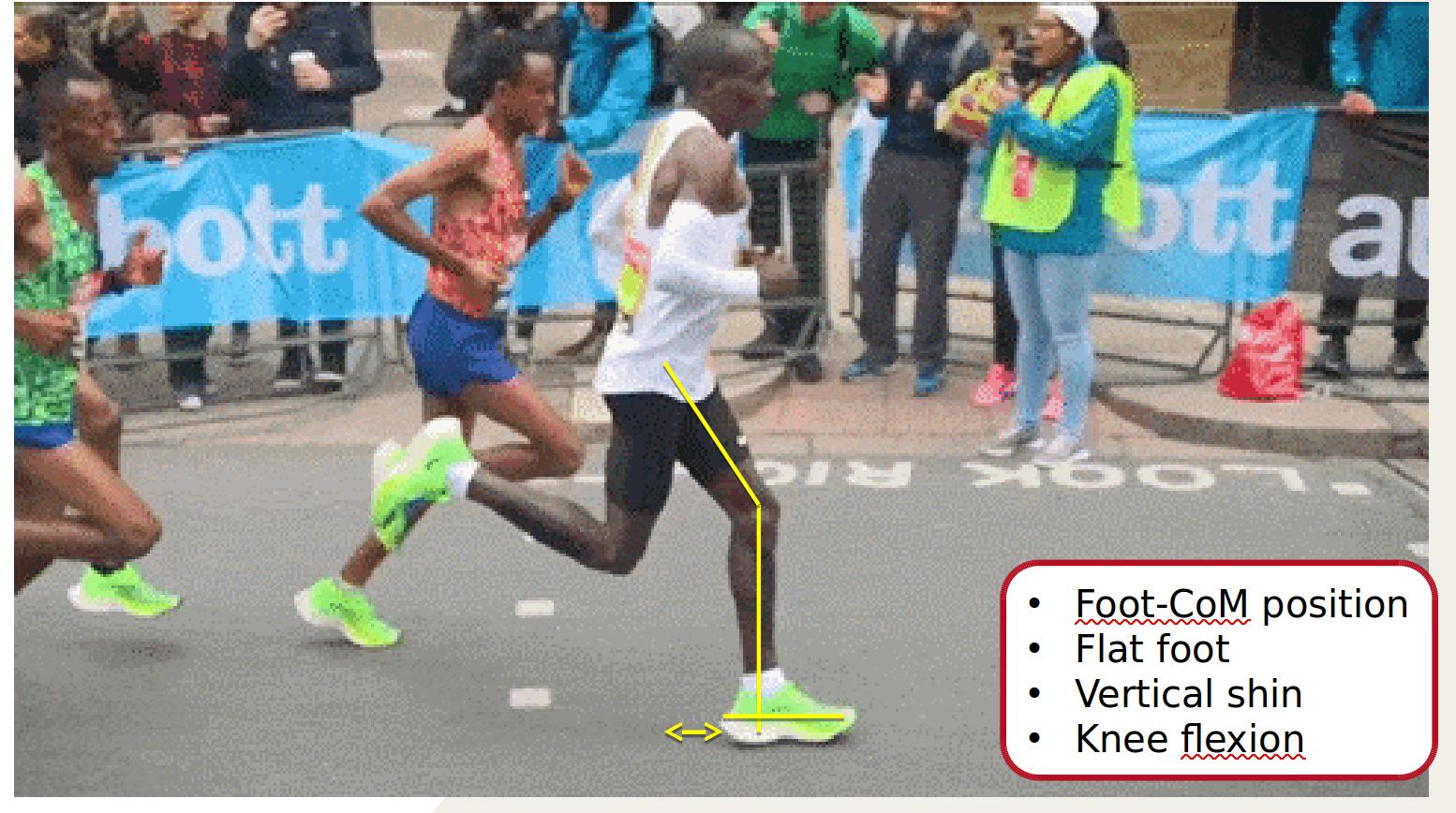

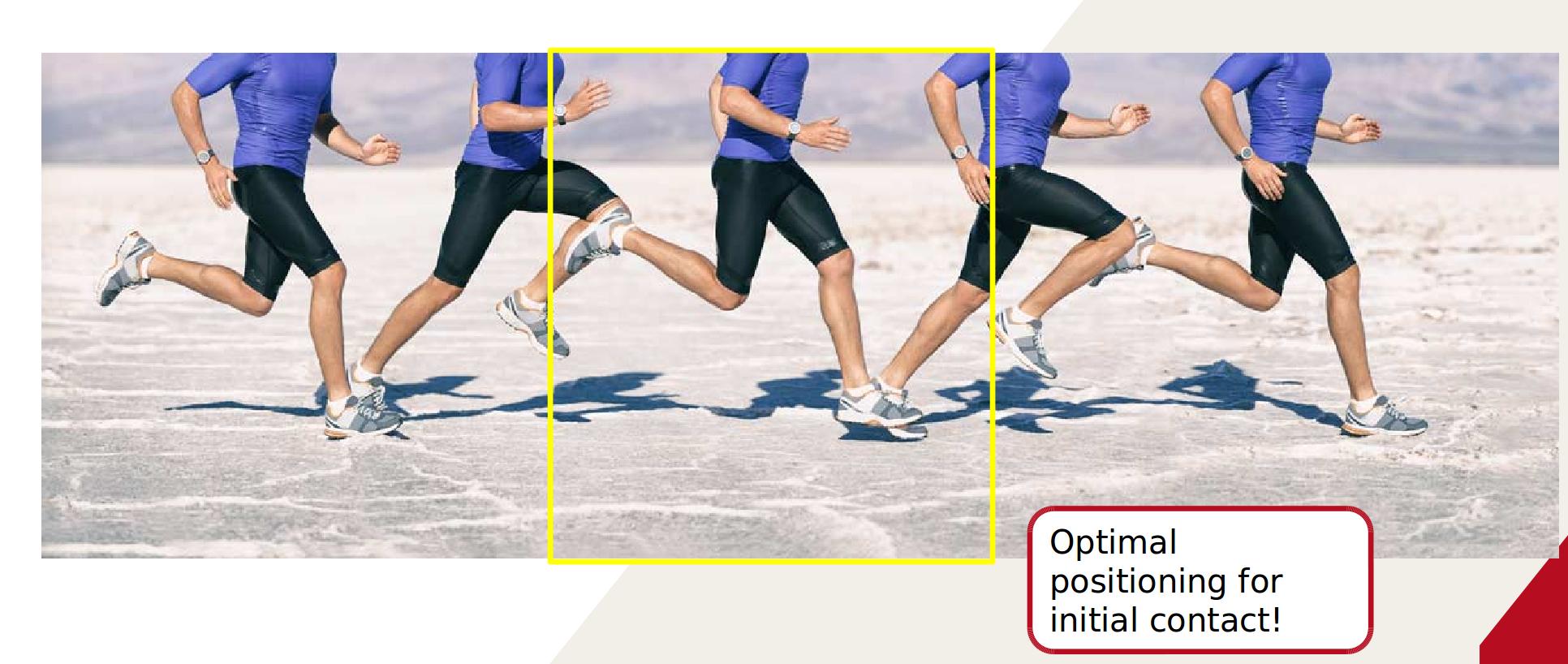
Mid Stance

Toe Off

Toe Off

Kinematics Charts
Pelvis
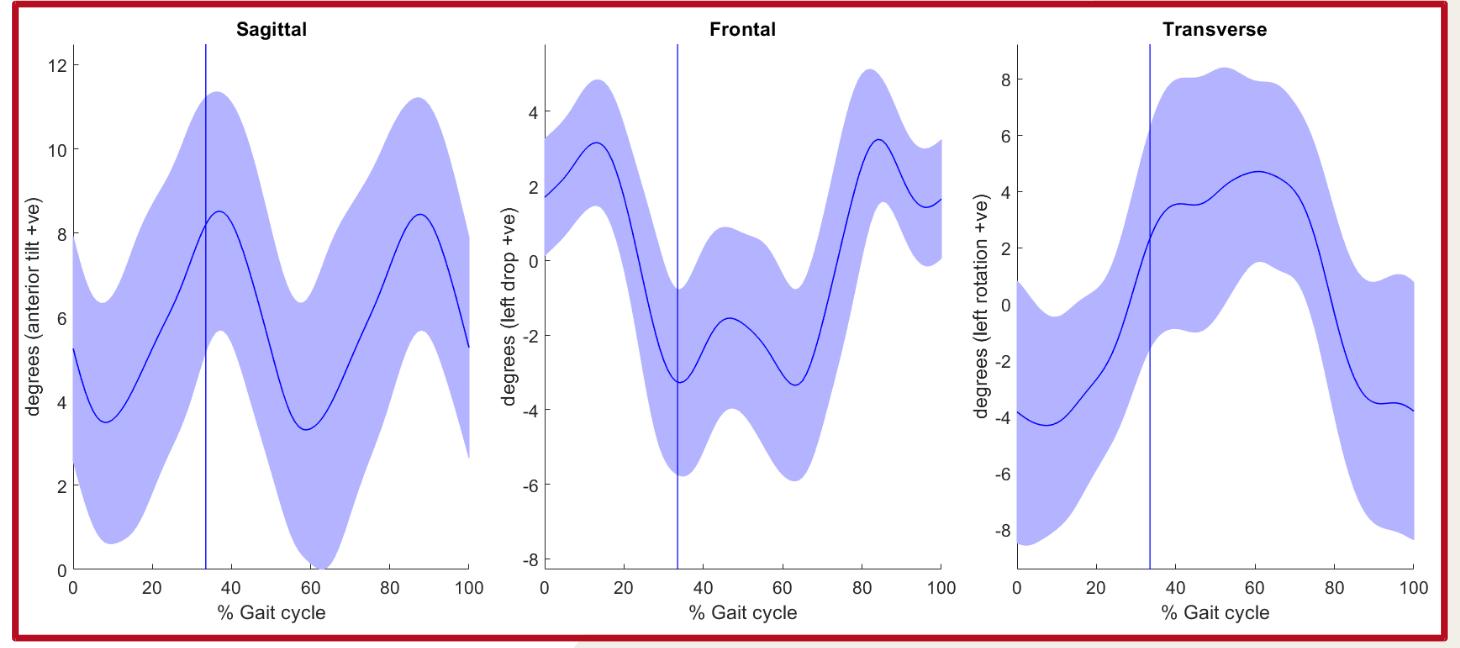
Hip
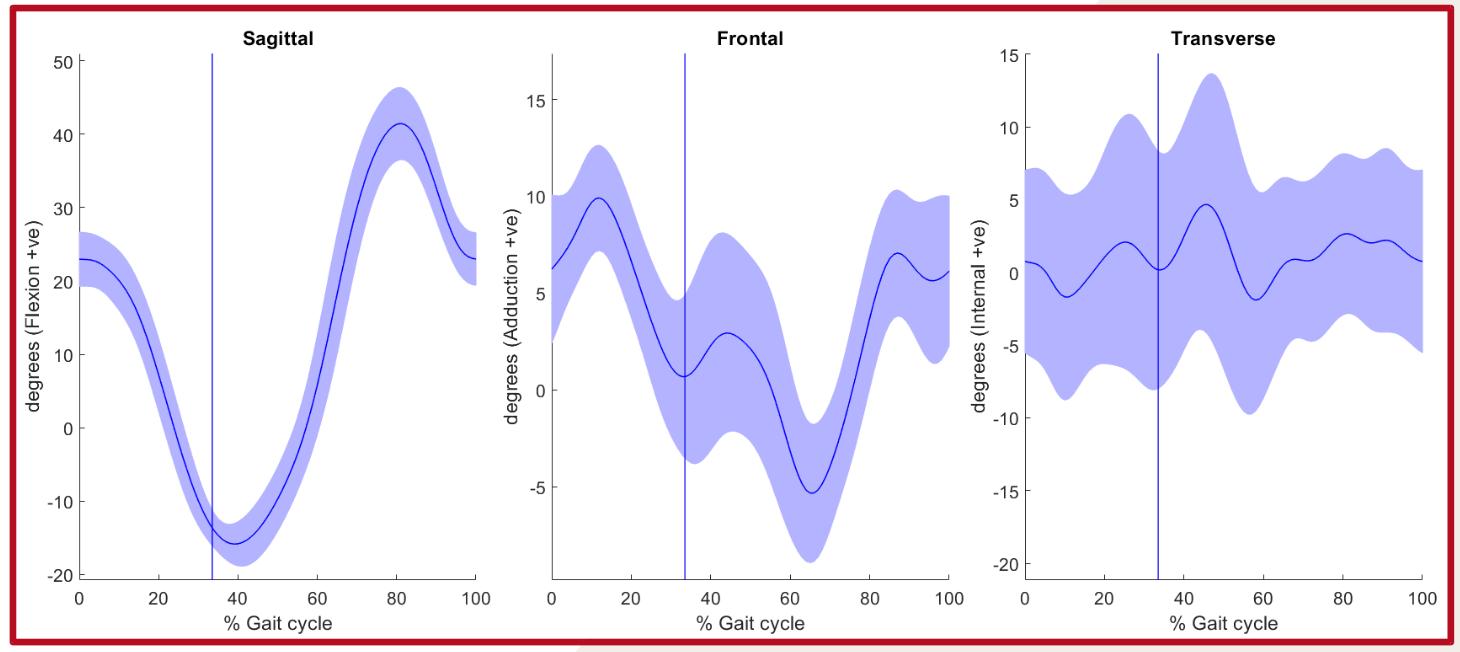
Knee
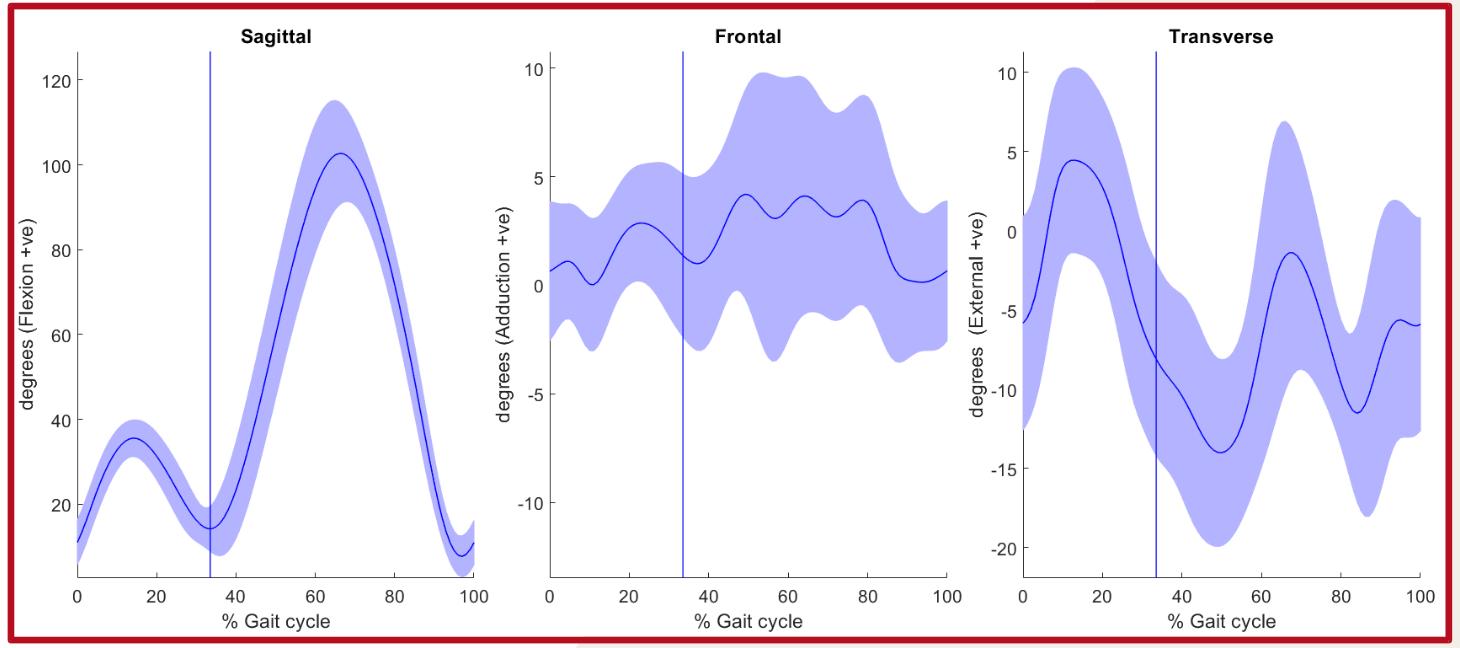
Ankle
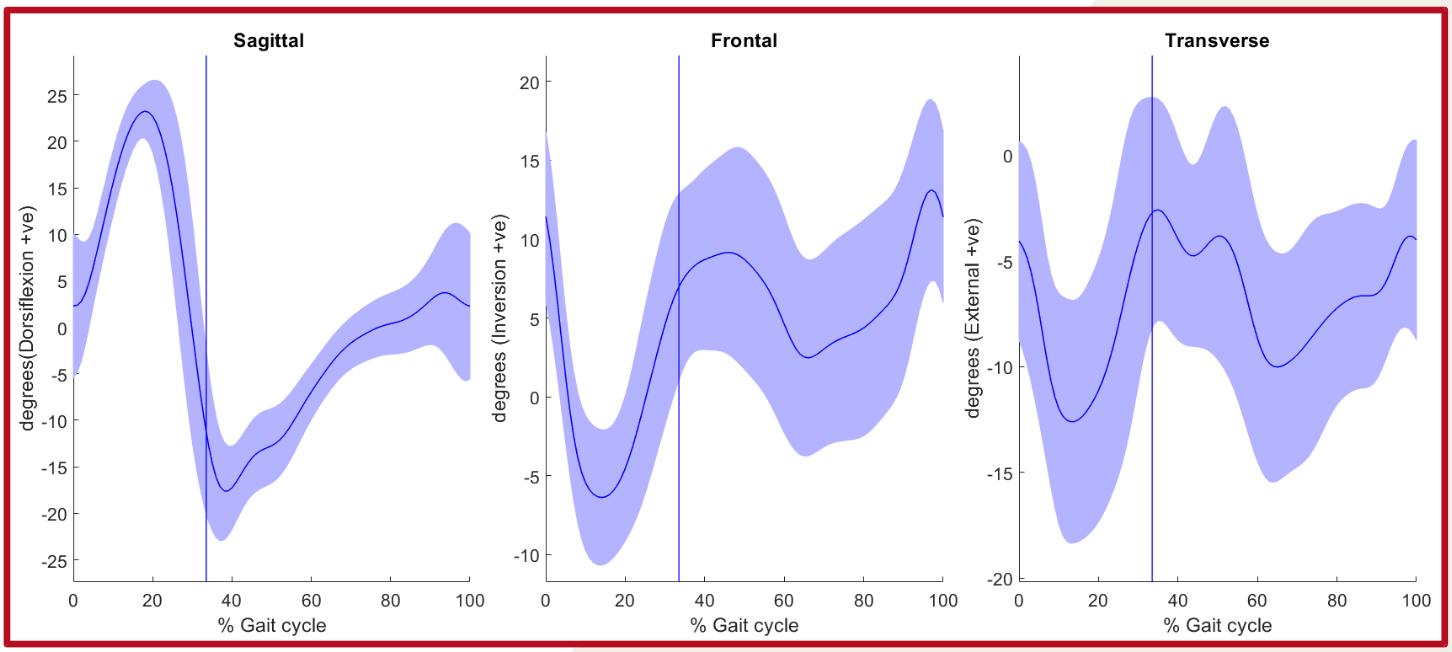
Foot Strike Patterns
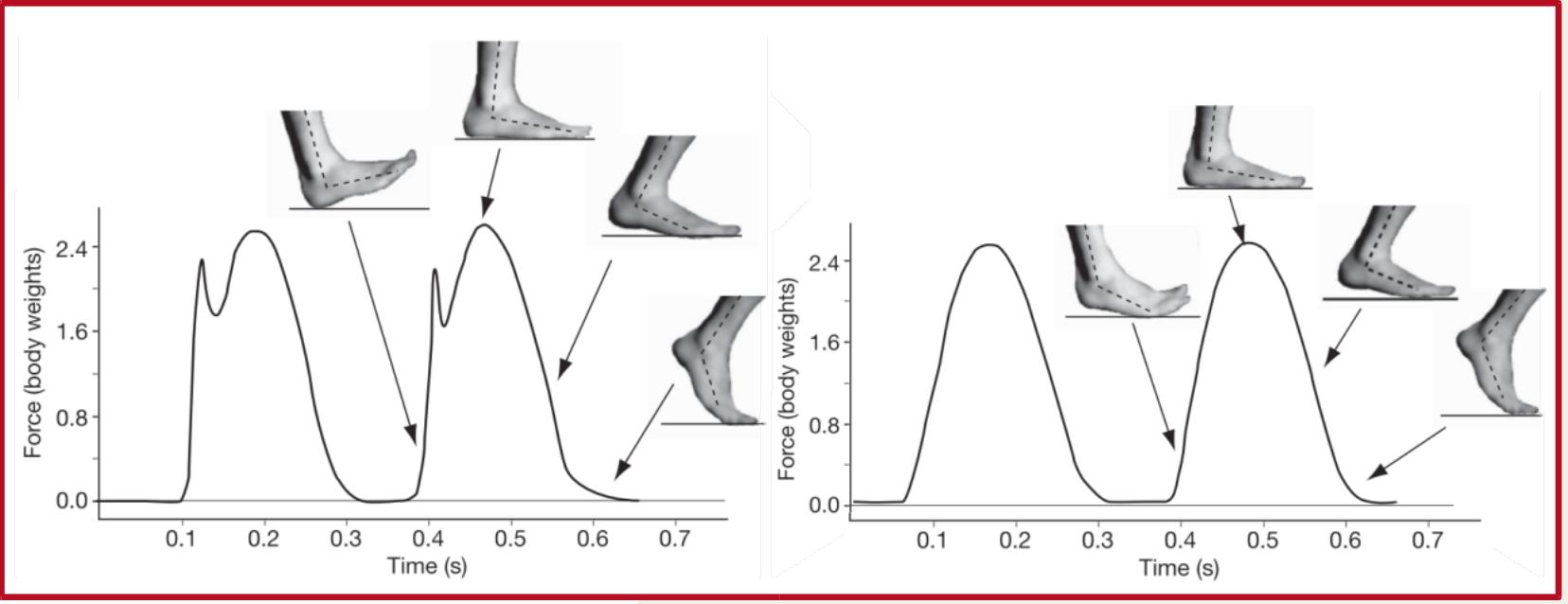
Amputee Locomotion
Baum et al. 2016
Non-amputated limbs experience increased mechanical loading compared with prosthetic and control limbs.
Individuals with amputation may be at an increased risk of acute injury or joint degeneration in their intact limb.
Individuals with amputation produced propulsive impulses equivalent to intact and control limbs by generating longer periods of positive impulse and thus adapted to the force production limitations of a running-specific prosthesis.
Sports high activity prostheses
Key Principles and Challenges
- Weight (of user)
- Activity level
- Environment
- Materials
- Design
- Perceptions
- Safety
The Flex Foot
- Designed in 1985 by amputee and engineer Van Philips -> Phillips, V.L., Flex Foot, Inc., 1985. Composite prosthetic foot and leg. U.S. Patent 4,547,913.
- Now commonly associated with the Paralympic games and sports prosthetics
- Energy storing / return type of prosthetic foot

Sport and High Activity Knees

Key Points from Previous Surveys
Deans, S., Burns, D., McGarry, A., Murray, K. and Mutrie, N., 2012. Motivations and barriers to prosthesis users participation in physical activity, exercise and sport: a review of the literature. Prosthetics and orthotics international, 36(3), pp.260-269)
General paucity in the amount of literature available on this area
Lack of activity in amputees and prosthesis users with regard to sports and activities
Kars C, Hofman M, Geertzen J, Pepping G and Dekker R., 2009. Participation in sports by lower limb amputees in the Province of Drenthe, Netherlands. Prosthet Orthot Int 33(4): pp 356–367.
68% of amputees inactive
Bragaru, M., Dekker, R., Geertzen, J.H. and Dijkstra, P.U., 2011. Amputees and sports. Sports medicine, 41(9), pp.721-740.
Sports were associated with a beneficial effect on the cardiopulmonary system, psychological well-being, social reintegration and physical functioning
LimbPower 2016
Current Prostheses Provision
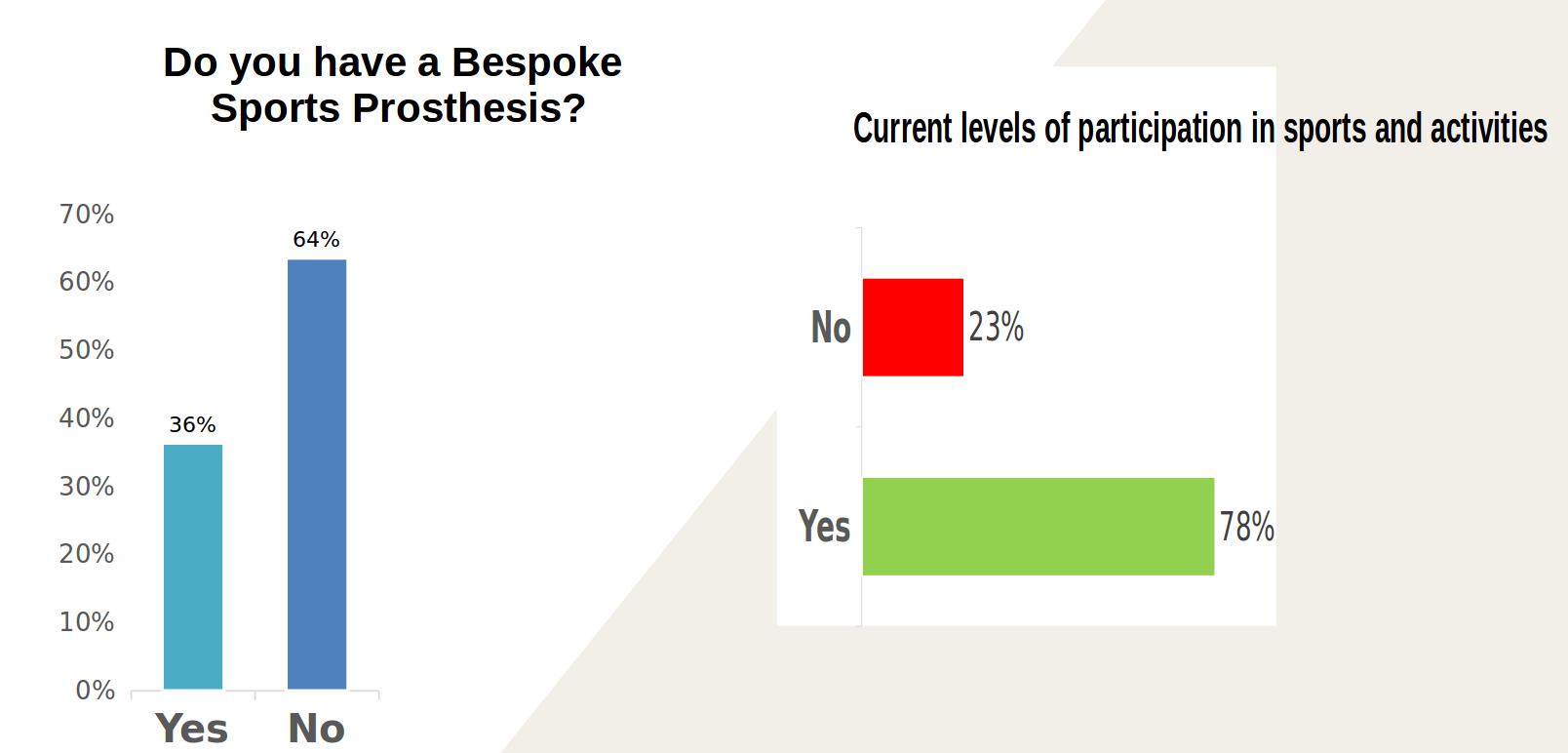
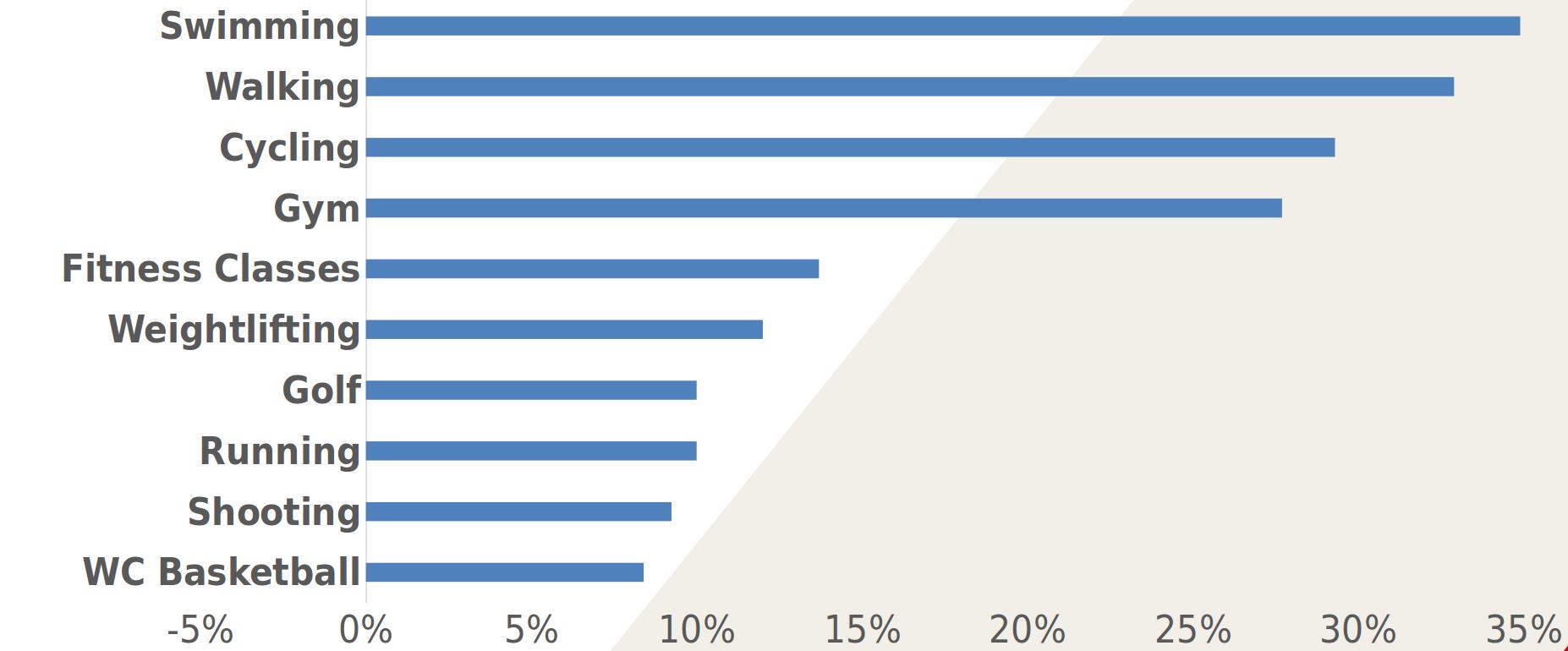
Activities undertaken / Participant %
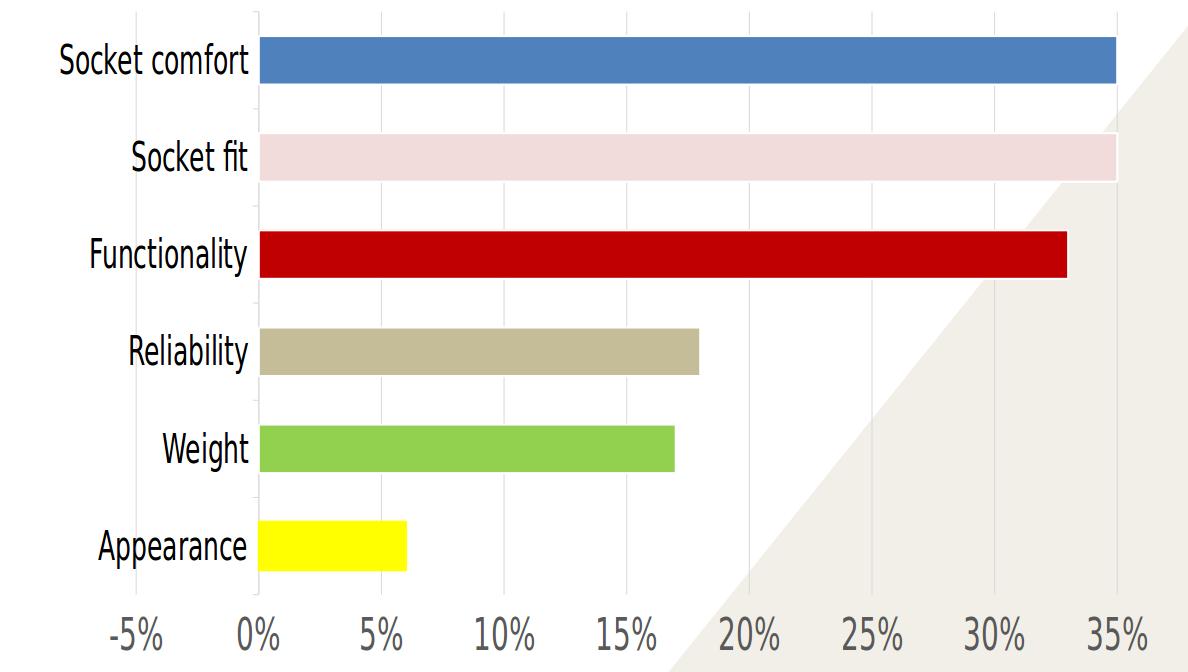
Factors Important to Prosthesis Use in Sports
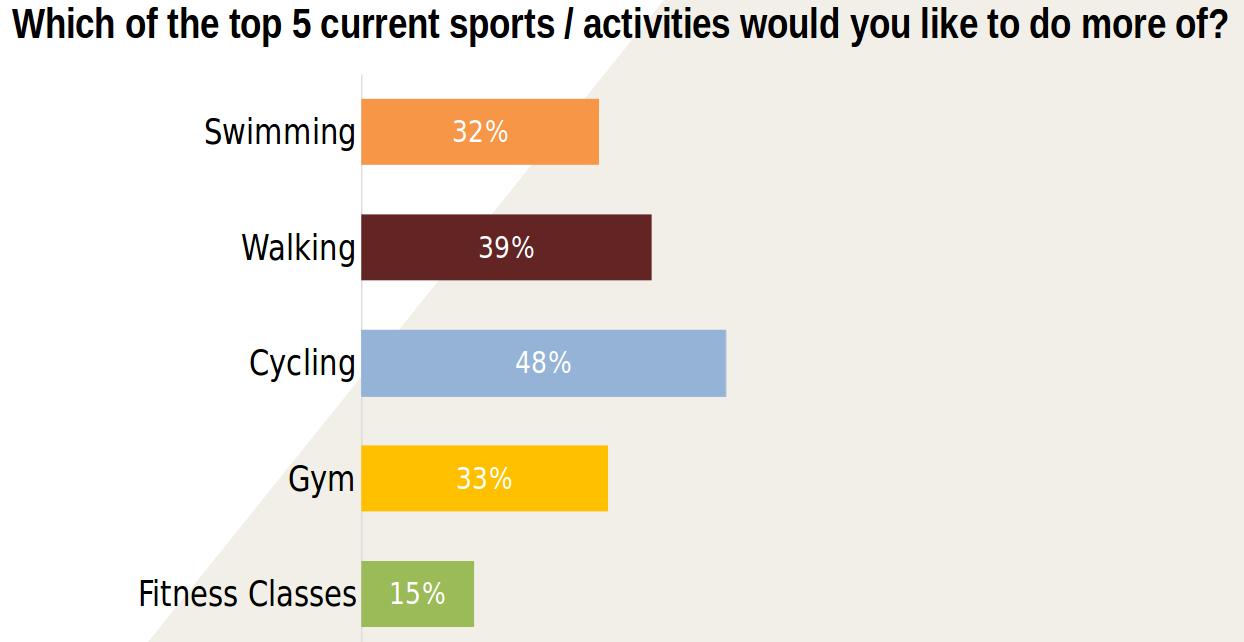
Increasing Participation
Task Specific Prostheses: Key Considerations for Cycling
Safety and performance!
We need to understand what is required to cycle effectively, and link this knowledge to the optimum prosthesis design Think about prosthesis position and/or attachment to the cycle, socket design, prosthesis alignment, the transmission of power and the flexibility (or otherwise) of the joints at key points during the ‘cycle’
References
Dorn, T. W., A. G. Schache and M. G. Pandy (2012). “Muscular strategy shift in human running: dependence of running speed on hip and ankle muscle performance.” J Exp Biol 215(Pt 11): 1944-1956.
Baum, B. S., H. Hobara, Y. H. Kim and J. K. Shim (2016). “Amputee Locomotion: Ground Reaction Forces During Submaximal Running With Running-Specific Prostheses.” 32(3): 287.
Hobara, H., B. S. Baum, H.-J. Kwon, A. Linberg, E. J. Wolf, R. H. Miller and J. K. Shim (2014). “Amputee locomotion: Lower extremity loading using running-specific prostheses.” Gait & Posture 39(1): 386-390.
Kehler, A. L., E. Hajkova, H. C. Holmberg and R. Kram (2014). “Forces and mechanical energy fluctuations during diagonal stride roller skiing; running on wheels?” Journal of Experimental Biology 217(21): 3779-3785.
Kulmala, J.-P., J. Kosonen, J. Nurminen and J. Avela (2018). “Running in highly cushioned shoes increases leg stiffness and amplifies impact loading.” Scientific Reports 8(1): 17496.
Lieberman, D. E., M. Venkadesan, W. A. Werbel, A. I. Daoud, S. D’Andrea, I. S. Davis, R. O. Mang’Eni and Y. Pitsiladis (2010). “Foot strike patterns and collision forces in habitually barefoot versus shod runners.” Nature 463(7280): 531-535.
Zahedi, S. (Proceedings of the XII International Congress of INTERBOR; Sept 22-25; Lisbon (Portugal))The results of the field trial of the Endolite Intelligent Prosthesis. ; 1993